If your company handles customer data—especially in the cloud—there’s a good chance you’ve been asked for a SOC 2. But what is it? But what does that actually mean?
A SOC 2 is an independent audit report issued by a licensed CPA firm. It shows that your organization has controls in place to protect systems and data. SOC 2 is designed for service providers like SaaS companies, cloud platforms, managed IT services, and data centers.
There are two types of SOC 2 reports:
- Type I looks at whether your controls are designed properly as of a specific date.
- Type II goes further and evaluates whether the controls are working as intended over time, usually over a period of several months.
SOC 2 isn’t a certification. It’s an attestation from an independent CPA firm that your controls meet the selected criteria. Many companies, especially larger ones, expect a Type II SOC 2 report before they’ll do business with a vendor.
Unlike certifications with a fixed checklist, SOC 2 is based on a set of flexible criteria called the Trust Services Criteria (TSC), developed by the AICPA. These criteria focus on how your company manages risk and protects systems and data. There are five possible areas: Security, Availability, Processing Integrity, Confidentiality, and Privacy. None of them are strictly required, but Security is commonly included because it covers general protections like access controls and system monitoring that are relevant to most services. Organizations select the TSCs that align with the risks they manage and the needs of their customers, allowing the report to reflect what matters most for their environment.
Trust Service Criteria Explained
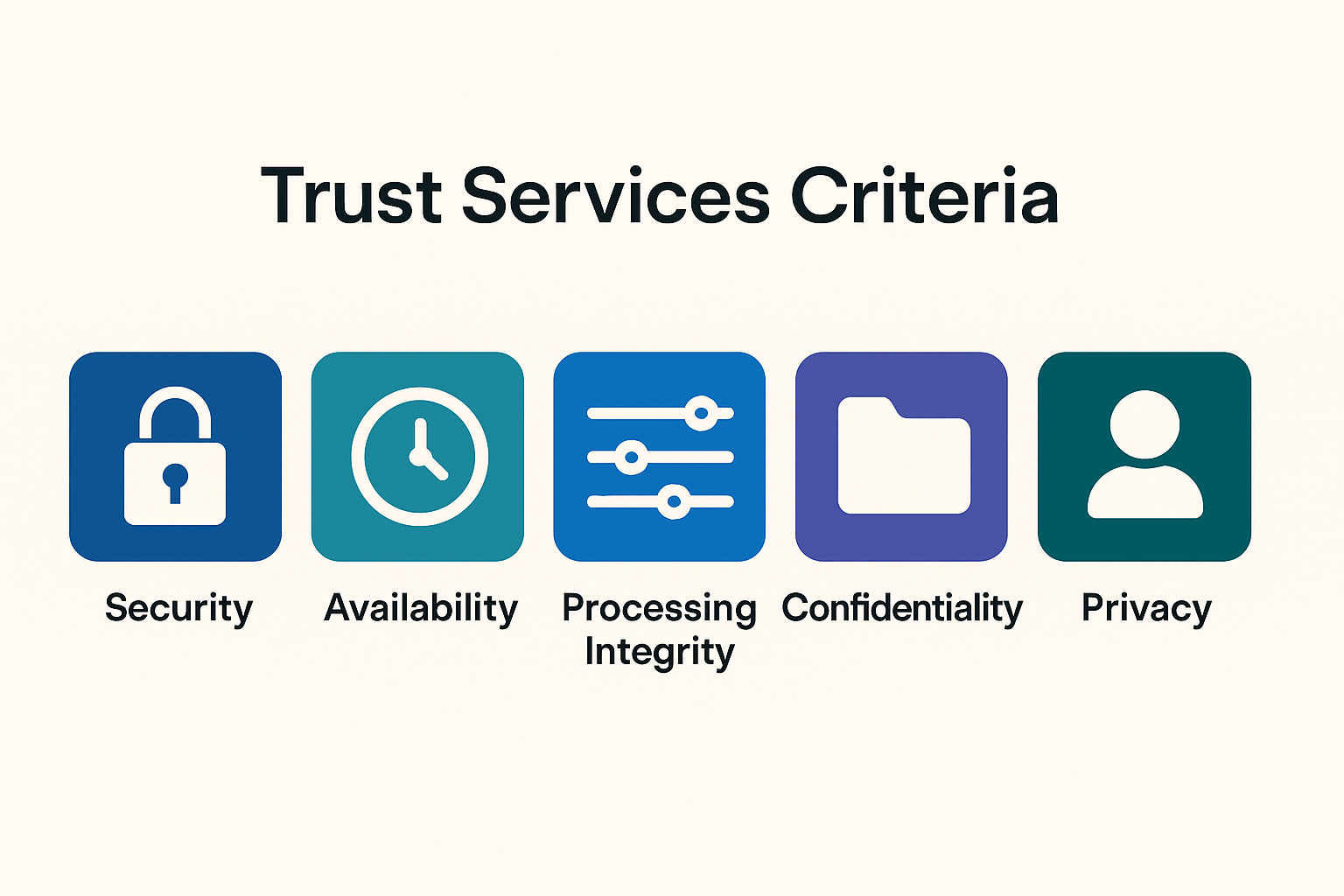
1. Security
This is typical and common to see in any SOC 2 Report. The Security TSC is all about protecting information and systems. This focuses on preventing unauthorized access. It includes things like firewalls, authentication, and system monitoring. The security TSC covers the basic controls that protect systems and data from unauthorized access, such as firewalls, multi-factor authentication, and intrusion detection. Security is a foundational criteria seen in SOC 2 reports.
2. Availability
This relates to whether your systems are up and running when customers need them. It includes performance monitoring, disaster recovery, and incident response. A cloud-based electronic health records (EHR) platform would likely include the Availability Trust Services Criteria in its SOC 2 report. Healthcare providers rely on constant access to patient records for critical care, so the system must have strong uptime commitments, disaster recovery processes, and performance monitoring in place to meet those expectations.
3. Processing Integrity
This covers the accuracy, completeness, and timeliness of data processing. It’s especially important for systems that automate transactions or provide data outputs. If its a system where customer are expecting payments/records to be processed accurately, completely, and in the correct order. Controls like input validation, transaction logging, and reconciliation processes help ensure that the system functions as intended without errors or delays.
4. Confidentiality
Probably the second most popular TSC after Security. Confidentiality is all about protecting sensitive information such as business plans, financials, or trade secrets. Typically its where you have IT systems offering services or platforms that store sensitive customer documents, contracts, and case files that must be protected from unauthorized access.Encryption, strict access controls, and secure data transmission help ensure that only authorized users can view or handle confidential information.
5. Privacy
This deals with how you collect, use, store, and dispose of personal information. It’s particularly important if your service handles personally identifiable information (PII). Unlike Confidentiality, which protects sensitive business information from unauthorized access, Privacy focuses on how personal data is collected, used, stored, and shared in accordance with the organization’s privacy notice and applicable laws. Controls for Privacy include user consent management, data minimization, and procedures for handling user data requests or deletion.
Most companies start by focusing on Security, then add other areas depending on customer expectations or the type of data involved. For example, a healthcare company might also include Privacy, while a payment processor might focus more on Processing Integrity and Confidentiality. Generally, it depends on the type of services offered and what risks your customers are concerned with.
Why SOC 2 Compliance Matters
Getting SOC 2 compliant helps you build trust with your customers and shows you’re serious about protecting their data. It shows that you have put the right controls in place and that those controls have been independently tested. For any company handling sensitive information, it’s a meaningful step toward being more transparent, reliable, and aligned with what clients expect. If you’re thinking about a SOC 2, we can help you get started.

At Sage Audits, We Work With You
We know audits can be overwhelming. Our goal is to make the process smoother, more understandable, and less stressful. We stand beside you with practical guidance—not just paperwork.
Whether it’s your first SOC 2 or a renewal, we’re here to help you get through it confidently and with real value. – Jordan Novak, Managing Partner



